Past Perfect Tense
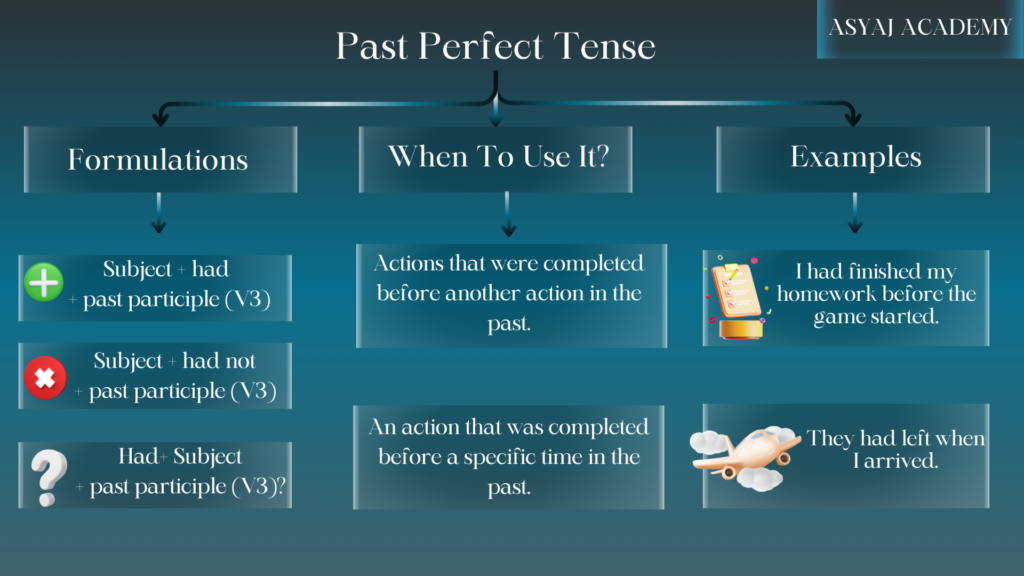
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that were completed before another action or point in the past. It helps to show the sequence of events in the past. Let’s explore its uses, form, and common time expressions.
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
1.Completed Actions Before Another Past Action:
- To describe an action that was finished before another past action.
- Example: “She had finished her homework before she watched TV.
2.Reported Speech:
- When reporting what someone said, thought, or felt, if it relates to an earlier time.
- Example: “He said that he had seen the movie.”
3.Unrealized Past Hopes or Wishes:
- To express a wish or hope that was not realized in the past.
- Example: “I had hoped to see her, but she had already left.”
Forming the Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense is formed using the past tense of the verb “to have” (had) and the past participle of the main verb.
Structure:
Affirmative: Subject + had + past participle
- Example: “They had visited the museum.”
Negative: Subject + had + not + past participle
- Example: “She had not completed her assignment.”
Question: Had + subject + past participle?
- Example: “Had he finished his dinner?”
Common Time Expressions
The Past Perfect Tense often uses specific time expressions to indicate the sequence of events:
1.Before:
- Used to indicate that one action happened earlier than another.
- Example: “He had left before she arrived.”
2.By the time:
- Used to indicate the specific point in the past by which an action was completed.
- Example: “By the time we got to the station, the train had already left.”
3.When:
- Used to show the relationship between two past events.
- Example: “When I arrived at the party, everyone had gone.”
4.Already:
- Used to emphasize that something had happened earlier than expected.
- Example: “She had already finished her homework when I called.”
5.Just:
- Used to indicate that something happened very shortly before another event.
- Example: “They had just left when we arrived.”
6.Until/By the time:
- Used to indicate that an action was ongoing until another action occurred.
- Example: “He had waited until she finished speaking.”
Examples in Context
To help you understand how to use the Past Perfect Tense, let’s look at these examples:
Before: “She had cooked dinner before they arrived.”
This indicates that the action of cooking dinner was completed before their arrival.
- By the time: “By the time we arrived, the show had started.”
This shows that the show started before we arrived.
- When: “When we reached the theater, the movie had begun.”
This indicates that the movie began before we reached the theater.
- Already: “They had already left when I got there.”
This emphasizes that they left earlier than the time I got there.
- Just: “I had just finished my homework when the phone rang.”
This shows that finishing the homework happened very shortly before the phone rang.
- Until: “He had lived in Paris until he moved to London.”
This indicates that living in Paris continued up to the point when he moved to London.
The Past Perfect Tense is useful for showing the sequence of events and clarifying which action happened first. It helps to provide a clear timeline of past events and is especially important in storytelling and reporting past experiences.