Present Perfect Tense
Uses of the Present Perfect Tense
Experience:
- To talk about experiences up to the present.
- Example: “I have visited Paris three times.”
Change Over Time:
- To describe changes that have occurred over a period of time.
- Example: “The city has grown significantly in the last few years.”
Accomplishments:
- To mention achievements or completed actions.
- Example: “She has finished her degree.”
Unfinished Actions:
- To discuss actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
- Example: “We have lived here since 2010.”
Recent Actions:
- To talk about recent events that are relevant now.
- Example: “They have just arrived.”
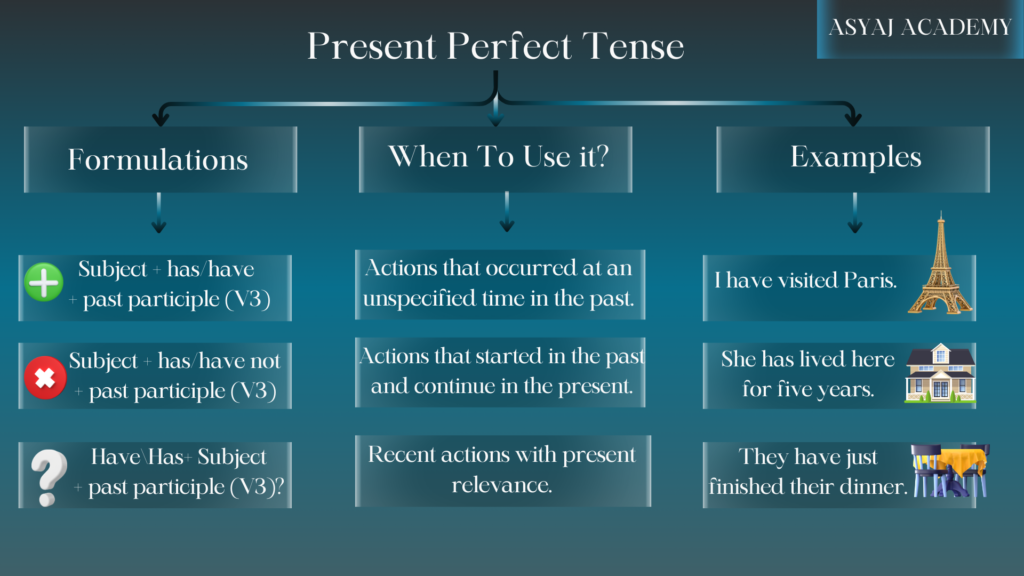
Forming the Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is formed using the present tense of the verb “to have” (have/has) and the past participle of the main verb.
Structure:
-
Affirmative: Subject + have/has + past participle
- Example: “She has traveled to Japan.”
-
Negative: Subject + have/has + not + past participle
- Example: “He has not finished his homework.”
-
Question: Have/Has + subject + past participle?
- Example: “Have you seen this movie?”
Common Time Expressions
Ever
Used in questions to ask if something has happened at any time up to now.
- Example: “Have you ever tried sushi?”
- Explanation: This asks if, at any point in your life, you have had the experience of trying sushi.
Never
Used to indicate that something has not happened at any time up to now.
- Example: “I have never been to Australia.”
- Explanation: This means that at no point in your life have you visited Australia.
Already
Used to emphasize that something has happened sooner than expected.
- Example: “They have already left.”
- Explanation: This means they left earlier than the speaker expected.
Just
Used to indicate that something happened very recently.
- Example: “She has just finished her meal.”
- Explanation: This means she finished her meal only a short time ago.
Yet
Used in questions and negative sentences to talk about something that is expected to happen.
- Example: “Has he called yet?” / “He hasn’t called yet.”
- Explanation: In the question, it asks if the call has happened up to now. In the negative sentence, it indicates that the call has not happened up to now, but it is still expected.
For
Used to talk about the duration of an action or situation.
- Example: “We have known each other for ten years.”
- Explanation: This indicates that the action of knowing each other started ten years ago and continues up to the present.
Since
Used to indicate the starting point of an action or situation that continues to the present.
- Example: “She has lived here since 2015.”
- Explanation: This means she started living here in 2015 and still lives here now.
Recently/Lately
Used to describe actions or situations that happened in the recent past.
- Example: “I have recently started a new job.” / “Lately, she has been very busy.”
- Explanation: These expressions indicate that the action of starting a new job or being busy happened in the near past.
Examples in Context
To give you a clearer understanding, let’s look at these expressions in full sentences:
Ever: “Have you ever visited the Grand Canyon?”
- Here, “ever” is used to ask about any time in the past up to now.
Never: “He has never failed a test.”
- “Never” emphasizes that there has been no instance of failing a test.
Already: “She has already completed her assignment.”
- “Already” shows that the assignment was finished sooner than expected.
Just: “They have just arrived.”
- “Just” indicates that their arrival happened a very short time ago.
Yet: “Have you finished your homework yet?” / “I haven’t finished my homework yet.”
- “Yet” is used to ask if the homework is completed up to now or to indicate it is not finished but expected to be done.
For: “We have lived in this city for five years.”
- “For” indicates the duration of living in the city, from the past up to now.
Since: “I have worked at this company since 2010.”
- “Since” shows the starting point of working at the company, continuing to the present.
Recently/Lately: “I have recently joined a new gym.” / “Lately, he has been feeling tired.”
Both “recently” and “lately” describe actions or states that have occurred in the recent past.
These time expressions help make the Present Perfect Tense more precise and meaningful in connecting past actions or states to the present moment.